Body
Octopus is a mixed architecture Intel/AMD Beowulf cluster with the following specifications:
Operating system
All the nodes of Octopus run Linux (CentOS 7).
The following types of jobs can be run on the cluster:
- batch jobs (no user interaction)
- GPU jobs (e.g scientific computing using GPGPUs or deep learning)
- memory intensive jobs (up to 256GB RAM on a single machine available as a SMP host)
- IO intensive jobs using the scratch partition (e.g several TB processing per job)
- Interactive Jupyer jobs running on the compute hosts
- Fully interactive desktop environment running on a compute node
Scheduler
The scheduler used in Octopus is open source SLURM For more information on using the scheduler please consult the SLURM cheatsheet
Partitions
There are three main types of partitions available for users:
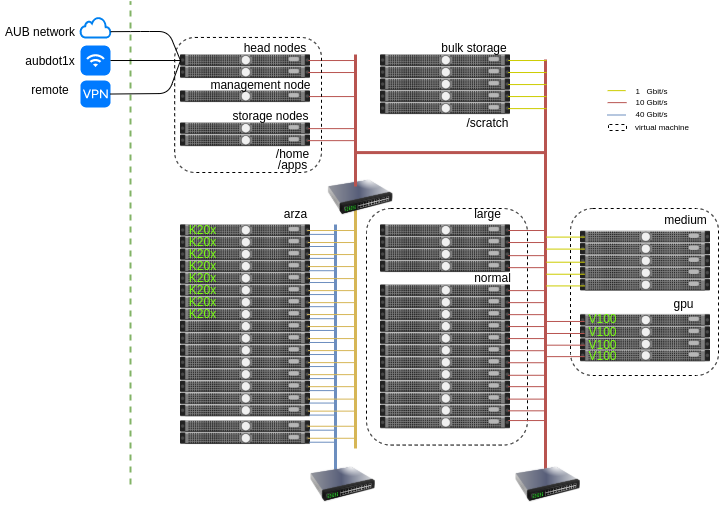
normal: 12 hosts with 16 vCPUs each with 64GB RAMgpu: 3 hosts with one V100 card on each node limited to 8 cores and 128 GB RAM max.large: 4 hosts with 64 cores each and 256 GB RAMarza: 16 hosts with 16 cores each and 64 GB RAM connected with Infiniband connectivitymedium: 5 hosts with 12 cores each and 24 GB RAM
For more information on using the paritions with the information on the resources and time limits please consult the hosts and partitions section.
Storage
All the hosts’ mount the /home directory and the /apps directory. The quota of the home directory is set to 25 GB. The /home directory is backed up regularly. For larger storage space the /scratch partition can be used that has a quota 1 TB per user. The maximum number of files that can be owned by a user is 1,000,000.